2019年
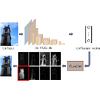
When working out, it is necessary to perform the same action many times for it to
have effect. If the action, such as squats or bench pressing, is performed with
poor form, it can lead to serious injuries in the long term. For this purpose, we
present an action dataset of squats where different types of poor form have been
annotated with a diversity of users and backgrounds, and propose a model, based on
temporal distance matrices, for the classification task. We first run a 3D pose
detector, then we normalize the pose and compute the distance matrix, in which each
element represents the distance between two joints. This representation is
invariant to differences in individuals, global translation, and global rotation,
allowing for high generalization to real world data. Our classification model
consists of a CNN with 1D convolutions. Results show that our method significantly
outperforms existing approaches for the task.
@InProceedings{OgataCVPRW2019,
author = {Ryoji Ogata and Edgar Simo-Serra and Satoshi Iizuka and Hiroshi Ishikawa},
title = {{Temporal Distance Matrices for Squat Classification}},
booktitle = "Proceedings of the Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW)",
year = 2019,
}
The preparation of large amounts of high-quality training data has always been the
bottleneck for the performance of supervised learning methods. It is especially
time-consuming for complicated tasks such as photo enhancement. A recent approach
to ease data annotation creates realistic training data automatically with
optimization. In this paper, we improve upon this approach by learning
image-similarity which, in combination with a Covariance Matrix Adaptation
optimization method, allows us to create higher quality training data for enhancing
photos. We evaluate our approach on challenging real world photo-enhancement images
by conducting a perceptual user study, which shows that its performance compares
favorably with existing approaches.
@InProceedings{OmiyaCVPRW2019,
author = {Mayu Omiya and Yusuke Horiuchi and Edgar Simo-Serra and Satoshi Iizuka and Hiroshi Ishikawa},
title = {{Optimization-Based Data Generation for Photo Enhancement}},
booktitle = "Proceedings of the Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW)",
year = 2019,
}
Re-staining Pathology Images by FCNN
Masayuki Fujitani, Yoshihiko Mochizuki, Satoshi Iizuka, Edgar Simo-Serra,
Hirokazu Kobayashi, Chika Iwamoto, Kenoki Ohuchida, Makoto Hashizume, Hidekata
Hontani, Hiroshi Ishikawa
International Conference on Machine Vision Applications (MVA) , 2019
In histopathology, pathologic tissue samples are stained using one of various
techniques according to the desired features to be observed in microscopic
examination. One problem is that staining is irreversible. Once a tissue slice is
stained using a technique, it cannot be re-stained using another. In this work, we
propose a method for simulated re-staining using a Fully Convolutional Neural
Network (FCNN).We convert a digitally scanned pathology image of a sample, stained
using one technique, into another image with a different simulated stain. The
challenge is that the ground truth cannot be obtained: the network needs training
data, which in this case would be pairs of images of a sample stained in two
different techniques. We overcome this problem by using the images of consecutive
slices that are stained using the two distinct techniques, screening for
morphological similarity by comparing their density components in the HSD color
space. We demonstrate the effectiveness of the method in the case of converting
hematoxylin and eosin-stained images into Masson’s trichrome stained images.
@InProceedings{FujitaniMVA2019,
author = {Masayuki Fujitani and Yoshihiko Mochizuki and Satoshi Iizuka and Edgar Simo-Serra and Hirokazu Kobayashi and Chika Iwamoto and Kenoki Ohuchida and Makoto Hashizume and Hidekata Hontani and Hiroshi Ishikawa},
title = {{Re-staining Pathology Images by FCNN}},
booktitle = "International Conference on Machine Vision Applications (MVA, Oral)",
year = 2019,
}
We address the problem of conditional image generation of synthesizing a new image
of an individual given a reference image and target pose. We base our approach on
generative adversarial networks and leverage deformable skip connections to deal
with pixel-to-pixel misalignments, self-attention to leverage complementary
features in separate portions of the image, e.g., arms or legs, and spectral
normalization to improve the quality of the synthesized images. We train the
synthesis model with a nearest-neighbour loss in combination with a relativistic
average hinge adversarial loss. We evaluate on the Market-1501 dataset and show how
our proposed approach can surpass existing approaches in conditional image
synthesis performance.
@InProceedings{HoriuchiMVA2019,
author = {Yusuke Horiuchi and Edgar Simo-Serra and Satoshi Iizuka and Hiroshi Ishikawa},
title = {{Banknote Portrait Detection Using Convolutional Neural Network}},
booktitle = "International Conference on Machine Vision Applications (MVA)",
year = 2019,
}
2018年
We address the problem of automatic photo enhancement, in which the challenge is to
determine the optimal enhancement for a given photo according to its content. For
this purpose, we train a convolutional neural network to predict the best
enhancement for given picture. While such machine learning techniques have shown
great promise in photo enhancement, there are some limitations. One is the problem
of interpretability, i.e., that it is not easy for the user to discern what has
been done by a machine. In this work, we leverage existing manual photo enhancement
tools as a black-box model, and predict the enhancement parameters of that model.
Because the tools are designed for human use, the resulting parameters can be
interpreted by their users. Another problem is the difficulty of obtaining training
data. We propose generating supervised training data from high-quality professional
images by randomly sampling realistic de-enhancement parameters. We show that this
approach allows automatic enhancement of photographs without the need for large
manually labelled supervised training datasets.
@InProceedings{OmiyaSIGGRAPASIABRIEF2018,
author = {Mayu Omiya and Edgar Simo-Serra and Satoshi Iizuka and Hiroshi Ishikawa},
title = {{Learning Photo Enhancement by Black-Box Model Optimization Data Generation}},
booktitle = "SIGGRAPH Asia 2018 Technical Briefs",
year = 2018,
}
We present an interactive approach for inking, which is the process of turning a
pencil rough sketch into a clean line drawing. The approach, which we call the
Smart Inker, consists of several "smart" tools that intuitively react to user
input, while guided by the input rough sketch, to efficiently and naturally connect
lines, erase shading, and fine-tune the line drawing output. Our approach is
data-driven: the tools are based on fully convolutional networks, which we train to
exploit both the user edits and inaccurate rough sketch to produce accurate line
drawings, allowing high-performance interactive editing in real-time on a variety
of challenging rough sketch images. For the training of the tools, we developed two
key techniques: one is the creation of training data by simulation of vague and
quick user edits; the other is a line normalization based on learning from vector
data. These techniques, in combination with our sketch-specific data augmentation,
allow us to train the tools on heterogeneous data without actual user interaction.
We validate our approach with an in-depth user study, comparing it with
professional illustration software, and show that our approach is able to reduce
inking time by a factor of 1.8x while improving the results of amateur users.
@Article{SimoSerraSIGGRAPH2018,
author = {Edgar Simo-Serra and Satoshi Iizuka and Hiroshi Ishikawa},
title = {{Real-Time Data-Driven Interactive Rough Sketch Inking}}
journal = "ACM Transactions on Graphics (SIGGRAPH)",
year = 2018,
volume = 37,
number = 4,
}
FCNNを用いた病理画像の染色変換
藤谷 真之,望月 義彦,飯塚 里志,シモセラ エドガー,小林 裕和,岩本 千佳,大内田 研宙,橋爪 誠,本谷 秀堅,石川 博
第21回画像の認識・理解シンポジウム(MIRU、オーラル) [学生奨励賞], 2018
背景と反射成分の同時推定による画像の映り込み除去
佐藤 良亮,飯塚 里志,シモセラ エドガー,石川 博
第21回画像の認識・理解シンポジウム(MIRU、オーラル) [学生奨励賞], 2018
再帰型畳み込みニューラルネットワークによる航空写真の多クラスセグメンテーション
高橋 宏輝,飯塚 里志,シモセラ エドガー,石川 博
第21回画像の認識・理解シンポジウム(MIRU) , 2018
補正パラメータ学習による写真の高品質自動補正
近江谷 真由,シモセラ エドガー,飯塚 里志,石川 博
第21回画像の認識・理解シンポジウム(MIRU) , 2018
SSDによる郵便物ラベルの認識及び高速化
尾形 亮二,望月 義彦,飯塚 里志,シモセラ エドガー,石川 博
第21回画像の認識・理解シンポジウム(MIRU) , 2018
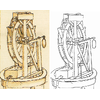
Learning to Restore Deteriorated Line Drawing
Kazuma Sasaki, Satoshi Iizuka, Edgar Simo-Serra, Hiroshi Ishikawa
The Visual Computer (Proc. of Computer Graphics International) , 2018
We propose a fully automatic approach to restore aged old line drawings. We
decompose the task into two subtasks: the line extraction subtask, which aims to
extract line fragments and remove the paper texture background, and the restoration
subtask, which fills in possible gaps and deterioration of the lines to produce a
clean line drawing. Our approach is based on a convolutional neural network that
consists of two sub-networks corresponding to the two subtasks. They are trained as
part of a single framework in an end-to-end fashion. We also introduce a new
dataset consisting of manually annotated sketches by Leonardo da Vinci which, in
combination with a synthetic data generation approach, allows training the network
to restore deteriorated line drawings. We evaluate our method on challenging
500-year-old sketches and compare with existing approaches with a user study, in
which it is found that our approach is preferred 72.7% of the time.
@Article{SasakiCGI2018,
author = {Sasaki Kazuma and Satoshi Iizuka and Edgar Simo-Serra and Hiroshi Ishikawa}},
title = {{Learning to Restore Deteriorated Line Drawing}},
journal = "The Visual Computer (Proc. of Computer Graphics International)",
year = {2018},
volume = {34},
number = {6-8},
pages = {1077-1085},
}
特集「漫画・線画の画像処理」ラフスケッチの自動線画化技術
シモセラ エドガー,飯塚 里志
映像情報メディア学会誌2018年5月号 , 2018
We present an integral framework for training sketch simplification networks that
convert challenging rough sketches into clean line drawings. Our approach augments
a simplification network with a discriminator network, training both networks
jointly so that the discriminator network discerns whether a line drawing is a real
training data or the output of the simplification network, which in turn tries to
fool it. This approach has two major advantages. First, because the discriminator
network learns the structure in line drawings, it encourages the output sketches of
the simplification network to be more similar in appearance to the training
sketches. Second, we can also train the simplification network with additional
unsupervised data, using the discriminator network as a substitute teacher. Thus,
by adding only rough sketches without simplified line drawings, or only line
drawings without the original rough sketches, we can improve the quality of the
sketch simplification. We show how our framework can be used to train models that
significantly outperform the state of the art in the sketch simplification task,
despite using the same architecture for inference. We additionally present an
approach to optimize for a single image, which improves accuracy at the cost of
additional computation time. Finally, we show that, using the same framework, it is
possible to train the network to perform the inverse problem, i.e., convert simple
line sketches into pencil drawings, which is not possible using the standard mean
squared error loss. We validate our framework with two user tests, where our
approach is preferred to the state of the art in sketch simplification 92.3% of the
time and obtains 1.2 more points on a scale of 1 to 5.
@Article{SimoSerraTOG2018,
author = {Edgar Simo-Serra and Satoshi Iizuka and Hiroshi Ishikawa},
title = {{Mastering Sketching: Adversarial Augmentation for Structured Prediction}},
journal = "Transactions on Graphics (Presented at SIGGRAPH)",
year = 2018,
volume = 37,
number = 1,
}
2017年
Content-aware image resizing aims to reduce the size of an image without touching
important objects and regions. In seam carving, this is done by assessing the
importance of each pixel by an energy function and repeatedly removing a string of
pixels avoiding pixels with high energy. However, there is no single energy
function that is best for all images: the optimal energy function is itself a
function of the image. In this paper, we present a method for predicting the
quality of the results of resizing an image with different energy functions, so as
to select the energy best suited for that particular image. We formulate the
selection as a classification problem; i.e., we 'classify' the input into the class
of images for which one of the energies works best. The standard approach would be
to use a CNN for the classification. However, the existence of a fully connected
layer forces us to resize the input to a fixed size, which obliterates useful
information, especially lower-level features that more closely relate to the
energies used for seam carving. Instead, we extract a feature from internal
convolutional layers, which results in a fixed-length vector regardless of the
input size, making it amenable to classification with a Support Vector Machine.
This formulation of the algorithm selection as a classification problem can be used
whenever there are multiple approaches for a specific image processing task. We
validate our approach with a user study, where our method outperforms recent seam
carving approaches.
@InProceedings{SasakiACPR2017,
author = {Kazuma Sasaki and Yuya Nagahama and Zheng Ze and Satoshi Iizuka and Edgar Simo-Serra and Yoshihiko Mochizuki and Hiroshi Ishikawa},
title = {{Adaptive Energy Selection For Content-Aware Image Resizing}},
booktitle = "Proceedings of the Asian Conference on Pattern Recognition (ACPR)",
year = 2017,
}
画像類似度を考慮したデータセットを用いて学習したCNNによる病理画像の染色変換
藤谷 真之,望月 義彦,飯塚 里志,シモセラ エドガー,石川 博
ヘルスケア・医療情報通信技術研究会(MICT) , 2017
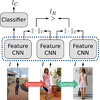
We present an approach to detect the main product in fashion images by exploiting
the textual metadata associated with each image. Our approach is based on a
Convolutional Neural Network and learns a joint embedding of object proposals and
textual metadata to predict the main product in the image. We additionally use
several complementary classification and overlap losses in order to improve
training stability and performance. Our tests on a large-scale dataset taken from
eight e-commerce sites show that our approach outperforms strong baselines and is
able to accurately detect the main product in a wide diversity of challenging
fashion images.
@InProceedings{RubioICCVW2017,
author = {Antonio Rubio and Longlong Yu and Edgar Simo-Serra and Francesc Moreno-Noguer},
title = {{Multi-Modal Embedding for Main Product Detection in Fashion}},
booktitle = "Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops (ICCVW)",
year = 2017,
}
We tackle the problem of multi-label classification of fashion images from noisy
data using minimal human supervision. We present a new dataset of full body poses,
each with a set of 66 binary labels corresponding to information about the garments
worn in the image and obtained in an automatic manner. As the automatically
collected labels contain significant noise, for a small subset of the data, we
manually correct the labels, using these correct labels for further training and
evaluating the model. We build upon a recent approach that both cleans the noisy
labels while learning to classify, and show simple changes that can significantly
improve the performance.
@InProceedings{InoueICCVW2017,
author = {Naoto Inoue and Edgar Simo-Serra and Toshihiko Yamasaki and Hiroshi Ishikawa},
title = {{Multi-Label Fashion Image Classification with Minimal Human Supervision}},
booktitle = "Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops (ICCVW)",
year = 2017,
}
In this work, we perform an experimental analysis of the differences of both how
humans and machines see and distinguish fashion styles. For this purpose, we
propose an expert-curated new dataset for fashion style prediction, which consists
of 14 different fashion styles each with roughly 1,000 images of worn outfits. The
dataset, with a total of 13,126 images, captures the diversity and complexity of
modern fashion styles. We perform an extensive analysis of the dataset by
benchmarking a wide variety of modern classification networks, and also perform an
in-depth user study with both fashion-savvy and fashion-naive users. Our results
indicate that, although classification networks are able to outperform naive users,
they are still far from the performance of savvy users, for which it is important
to not only consider texture and color, but subtle differences in the combination
of garments.
@InProceedings{TakagiICCVW2017,
author = {Moeko Takagi and Edgar Simo-Serra and Satoshi Iizuka and Hiroshi Ishikawa},
title = {{What Makes a Style: Experimental Analysis of Fashion Prediction}},
booktitle = "Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops (ICCVW)",
year = 2017,
}
Finding a product in the fashion world can be a daunting task. Everyday, e-commerce
sites are updating with thousands of images and their associated metadata (textual
information), deepening the problem, akin to finding a needle in a haystack. In
this paper, we leverage both the images and textual metadata and propose a joint
multi-modal embedding that maps both the text and images into a common latent
space. Distances in the latent space correspond to similarity between products,
allowing us to effectively perform retrieval in this latent space, which is both
efficient and accurate. We train this embedding using large-scale real world
e-commerce data by both minimizing the similarity between related products and
using auxiliary classification networks to that encourage the embedding to have
semantic meaning. We compare against existing approaches and show significant
improvements in retrieval tasks on a large-scale e-commerce dataset. We also
provide an analysis of the different metadata.
@InProceedings{RubioICIP2017,
author = {Antonio Rubio and Longlong Yu and Edgar Simo-Serra and Francesc Moreno-Noguer},
title = {{Multi-Modal Joint Embedding for Fashion Product Retrieval}},
booktitle = "International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP)",
year = 2017,
}
ディープラーニングによるファッションコーディネートの分類
高木 萌子,シモセラ エドガー,飯塚 里志,石川 博
第20回画像の認識・理解シンポジウム(MIRU) , 2017
再帰構造を用いた全層畳み込みニューラルネットワークによる航空写真における建物のセグメンテーション
高橋 宏輝,飯塚 里志,シモセラ エドガー,石川 博
第20回画像の認識・理解シンポジウム(MIRU、オーラル) [学生奨励賞], 2017

Globally and Locally Consistent Image Completion
Satoshi Iizuka, Edgar Simo-Serra, Hiroshi Ishikawa
ACM Transactions on Graphics (SIGGRAPH) , 2017
We present a novel approach for image completion that results in images that are
both locally and globally consistent. With a fully-convolutional neural network, we
can complete images of arbitrary resolutions by filling-in missing regions of any
shape. To train this image completion network to be consistent, we use global and
local context discriminators that are trained to distinguish real images from
completed ones. The global discriminator looks at the entire image to assess if it
is coherent as a whole, while the local discriminator looks only at a small area
centered at the completed region to ensure the local consistency of the generated
patches. The image completion network is then trained to fool the both context
discriminator networks, which requires it to generate images that are
indistinguishable from real ones with regard to overall consistency as well as in
details. We show that our approach can be used to complete a wide variety of
scenes. Furthermore, in contrast with the patch-based approaches such as
PatchMatch, our approach can generate fragments that do not appear elsewhere in the
image, which allows us to naturally complete the images of objects with familiar
and highly specific structures, such as faces.
@Article{IizukaSIGGRAPH2017,
author = {Satoshi Iizuka and Edgar Simo-Serra and Hiroshi Ishikawa},
title = {{Globally and Locally Consistent Image Completion}},
journal = "ACM Transactions on Graphics (SIGGRAPH)",
year = 2017,
volume = 36,
number = 4,
}
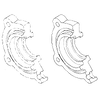
Joint Gap Detection and Inpainting of Line Drawings
Kazuma Sasaki, Satoshi Iizuka, Edgar Simo-Serra, Hiroshi Ishikawa
Conference in Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition
(CVPR) , 2017
We propose a novel data-driven approach for automatically detecting and completing
gaps in line drawings with a Convolutional Neural Network. In the case of existing
inpainting approaches for natural images, masks indicating the missing regions are
generally required as input. Here, we show that line drawings have enough
structures that can be learned by the CNN to allow automatic detection and
completion of the gaps without any such input. Thus, our method can find the gaps
in line drawings and complete them without user interaction. Furthermore, the
completion realistically conserves thickness and curvature of the line segments.
All the necessary heuristics for such realistic line completion are learned
naturally from a dataset of line drawings, where various patterns of line
completion are generated on the fly as training pairs to improve the model
generalization. We evaluate our method qualitatively on a diverse set of
challenging line drawings and also provide quantitative results with a user study,
where it significantly outperforms the state of the art.
@InProceedings{SasakiCVPR2017,
author = {Kazuma Sasaki Satoshi Iizuka and Edgar Simo-Serra and Hiroshi Ishikawa},
title = {{Joint Gap Detection and Inpainting of Line Drawings}},
booktitle = "Proceedings of the Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR)",
year = 2017,
}
ディープマリオ
北川 竜太郎,シモセラ エドガー,飯塚 里志,望月 義彦,石川 博
Visual Computing / グラフィクスとCAD 合同シンポジウム(オーラル) , 2017
回帰分析にもとづく補正モデルを用いた写真の自動補正
近江谷 真由,シモセラ エドガー,飯塚 里志,石川 博
Visual Computing / グラフィクスとCAD 合同シンポジウム(オーラル) , 2017
Banknotes generally have different designs according to their denominations. Thus,
if characteristics of each design can be recognized, they can be used for sorting
banknotes according to denominations. Portrait in banknotes is one such
characteristic that can be used for classification. A sorting system for banknotes
can be designed that recognizes portraits in each banknote and sort it accordingly.
In this paper, our aim is to automate the configuration of such a sorting system by
automatically detect portraits in sample banknotes, so that it can be quickly
deployed in a new target country. We use Convolutional Neural Networks to detect
portraits in completely new set of banknotes robust to variation in the ways they
are shown, such as the size and the orientation of the face.
@InProceedings{KitagawaMVA2017,
author = {Ryutaro Kitagawa and Yoshihiko Mochizuki and Satoshi Iizuka and Edgar Simo-Serra and Hiroshi Matsuki and Naotake Natori and Hiroshi Ishikawa},
title = {{Banknote Portrait Detection Using Convolutional Neural Network}},
booktitle = "International Conference on Machine Vision Applications (MVA)",
year = 2017,
}
Finding a product in the fashion world can be a daunting task. Everyday, e-commerce
sites are updating with thousands of images and their associated metadata (textual
information), deepening the problem. In this paper, we leverage both the images and
textual metadata and propose a joint multi-modal embedding that maps both the text
and images into a common latent space. Distances in the latent space correspond to
similarity between products, allowing us to effectively perform retrieval in this
latent space. We compare against existing approaches and show significant
improvements in retrieval tasks on a large-scale e-commerce dataset
@InProceedings{RubioVL2017,
author = {Antonio Rubio and Longlong Yu and Edgar Simo-Serra and Francesc Moreno-Noguer},
title = {{Multi-Modal Fashion Product Retrieval}},
booktitle = "The 6th Workshop on Vision and Language (VL)",
year = 2017,
}
2016年
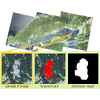
We present an approach for the detection of buildings in multispectral satellite
images. Unlike 3-channel RGB images, satellite imagery contains additional channels
corresponding to different wavelengths. Approaches that do not use all channels are
unable to fully exploit these images for optimal performance. Furthermore, care
must be taken due to the large bias in classes, e.g., most of the Earth is covered
in water and thus it will be dominant in the images. Our approach consists of
training a Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) from scratch to classify
multispectral image patches taken by satellites as whether or not they belong to a
class of buildings. We then adapt the classification network to detection by
converting the fully-connected layers of the network to convolutional layers, which
allows the network to process images of any resolution. The dataset bias is
compensated by subsampling negatives and tuning the detection threshold for optimal
performance. We have constructed a new dataset using images from the Landsat 8
satellite for detecting solar power plants and show our approach is able to
significantly outperform the state-of-the-art. Furthermore, we provide an in-depth
evaluation of the seven different spectral bands provided by the satellite images
and show it is critical to combine them to obtain good results.
@InProceedings{IshiiICPR2016,
author = {Tomohiro Ishii and Edgar Simo-Serra and Satoshi Iizuka and Yoshihiko Mochizuki and Akihiro Sugimoto and Hiroshi Ishikawa and Ryosuke Nakamura},
title = {{Detection by Classification of Buildings in Multispectral Satellite Imagery}},
booktitle = "Proceedings of the International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR)",
year = 2016,
}
We propose a new superpixel algorithm based on exploiting the boundary information
of an image, as objects in images can generally be described by their boundaries.
Our proposed approach initially estimates the boundaries and uses them to place
superpixel seeds in the areas in which they are more dense. Afterwards, we minimize
an energy function in order to expand the seeds into full superpixels. In addition
to standard terms such as color consistency and compactness, we propose using the
geodesic distance which concentrates small superpixels in regions of the image with
more information, while letting larger superpixels cover more homogeneous regions.
By both improving the initialization using the boundaries and coherency of the
superpixels with geodesic distances, we are able to maintain the coherency of the
image structure with fewer superpixels than other approaches. We show the resulting
algorithm to yield smaller Variation of Information metrics in seven different
datasets while maintaining Undersegmentation Error values similar to the
state-of-the-art methods.
@InProceedings{RubioICPR2016,
author = {Antonio Rubio and Longlong Yu and Edgar Simo-Serra and Francesc Moreno-Noguer},
title = {{BASS: Boundary-Aware Superpixel Segmentation}},
booktitle = "Proceedings of the International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR)",
year = 2016,
}
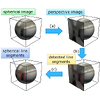
Room Reconstruction from a Single Spherical Image by Higher-order Energy
Minimization
Kosuke Fukano, Yoshihiko Mochizuki, Edgar Simo-Serra, Satoshi Iizuka, Akihiro
Sugimoto, Hiroshi Ishikawa
International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR) , 2016
We propose a method to reconstruct a simple room from a single spherical image,
i.e., to identify structural planes that form the ceiling, the floor, and the
walls. A spherical image records the light that falls on a single viewpoint from
all directions. Because there is no need to correlate geometrical information from
multiple images, it facilitates the robust reconstruction of precise structure of
the room. In our method, we first detect line segments in the image, which we then
classify into those that form the boundaries of the structural planes and those
that do not. The classification is a large combinatorial problem, which we solve
with graph cuts as a minimization problem of a higher-order energy that combines
the various measures of likelihood that one, two, or three line segments are part
of the boundary. Finally, we estimate the planes that constitute the room from the
line segments classified as residing on the boundaries. We evaluate the proposed
method on synthetic and real images.
@InProceedings{FukanoICPR2016,
author = {Kosuke Fukano and Yoshihiko Mochizuki and Edgar Simo-Serra and Satoshi Iizuka and Akihiro Sugimoto and Hiroshi Ishikawa},
title = {{Room Reconstruction from a Single Spherical Image by Higher-order Energy Minimization}},
booktitle = "Proceedings of the International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR)",
year = 2016,
}
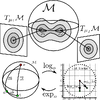
We present a novel approach for learning a finite mixture model on a Riemannian
manifold in which Euclidean metrics are not applicable and one needs to resort to
geodesic distances consistent with the manifold geometry. For this purpose, we draw
inspiration on a variant of the expectation-maximization algorithm, that uses a
minimum message length criterion to automatically estimate the optimal number of
components from multivariate data lying on an Euclidean space. In order to use this
approach on Riemannian manifolds, we propose a formulation in which each component
is defined on a different tangent space, thus avoiding the problems associated with
the loss of accuracy produced when linearizing the manifold with a single tangent
space. Our approach can be applied to any type of manifold for which it is possible
to estimate its tangent space. Additionally, we consider using shrinkage covariance
estimation to improve the robustness of the method, especially when dealing with
very sparsely distributed samples. We evaluate the approach on a number of
situations, going from data clustering on manifolds to combining pose and
kinematics of articulated bodies for 3D human pose tracking. In all cases, we
demonstrate remarkable improvement compared to several chosen baselines.
@Article{SimoSerraIJCV2016,
author = {Edgar Simo-Serra and Carme Torras and Francesc Moreno Noguer},
title = {{3D Human Pose Tracking Priors using Geodesic Mixture Models}},
journal = {International Journal of Computer Vision (IJCV)},
volume = {122},
number = {2},
pages = {388--408},
year = 2016,
}
Convolutional Neural Network による紙幣の肖像画検出
北川 竜太郎,望月 義彦,飯塚 里志,シモセラ エドガー,名取 直毅,松木 洋,石川 博
第19回画像の認識・理解シンポジウム(MIRU) , 2016
全層畳込みニューラルネットワークを用いた線画の自動補完
佐々木 一真,飯塚 里志,シモセラ エドガー,石川 博
第19回画像の認識・理解シンポジウム(MIRU) , 2016
In this paper, we present a novel technique to simplify sketch drawings based on
learning a series of convolution operators. In contrast to existing approaches that
require vector images as input, we allow the more general and challenging input of
rough raster sketches such as those obtained from scanning pencil sketches. We
convert the rough sketch into a simplified version which is then amendable for
vectorization. This is all done in a fully automatic way without user intervention.
Our model consists of a fully convolutional neural network which, unlike most
existing convolutional neural networks, is able to process images of any dimensions
and aspect ratio as input, and outputs a simplified sketch which has the same
dimensions as the input image. In order to teach our model to simplify, we present
a new dataset of pairs of rough and simplified sketch drawings. By leveraging
convolution operators in combination with efficient use of our proposed dataset, we
are able to train our sketch simplification model. Our approach naturally overcomes
the limitations of existing methods, e.g., vector images as input and long
computation time; and we show that meaningful simplifications can be obtained for
many different test cases. Finally, we validate our results with a user study in
which we greatly outperform similar approaches and establish the state of the art
in sketch simplification of raster images.
@Article{SimoSerraSIGGRAPH2016,
author = {Edgar Simo-Serra and Satoshi Iizuka and Kazuma Sasaki and Hiroshi Ishikawa},
title = {{Learning to Simplify: Fully Convolutional Networks for Rough Sketch Cleanup}},
journal = "ACM Transactions on Graphics (SIGGRAPH)",
year = 2016,
volume = 35,
number = 4,
}

Let there be Color!: Joint End-to-end Learning of Global and Local Image
Priors for Automatic Image Colorization with Simultaneous Classification
Satoshi Iizuka*, Edgar Simo-Serra*, Hiroshi Ishikawa (* equal contribution)
ACM Transactions on Graphics (SIGGRAPH) , 2016
We present a novel technique to automatically colorize grayscale images that
combines both global priors and local image features. Based on Convolutional Neural
Networks, our deep network features a fusion layer that allows us to elegantly
merge local information dependent on small image patches with global priors
computed using the entire image. The entire framework, including the global and
local priors as well as the colorization model, is trained in an end-to-end
fashion. Furthermore, our architecture can process images of any resolution, unlike
most existing approaches based on CNN. We leverage an existing large-scale scene
classification database to train our model, exploiting the class labels of the
dataset to more efficiently and discriminatively learn the global priors. We
validate our approach with a user study and compare against the state of the art,
where we show significant improvements. Furthermore, we demonstrate our method
extensively on many different types of images, including black-and-white
photography from over a hundred years ago, and show realistic colorizations.
@Article{IizukaSIGGRAPH2016,
author = {Satoshi Iizuka and Edgar Simo-Serra and Hiroshi Ishikawa},
title = {{Let there be Color!: Joint End-to-end Learning of Global and Local Image Priors for Automatic Image Colorization with Simultaneous Classification}},
journal = "ACM Transactions on Graphics (SIGGRAPH)",
year = 2016,
volume = 35,
number = 4,
}
We propose a novel approach for learning features from weakly-supervised data by
joint ranking and classification. In order to exploit data with weak labels, we
jointly train a feature extraction network with a ranking loss and a classification
network with a cross-entropy loss. We obtain high-quality compact discriminative
features with few parameters, learned on relatively small datasets without
additional annotations. This enables us to tackle tasks with specialized images not
very similar to the more generic ones in existing fully-supervised datasets. We
show that the resulting features in combination with a linear classifier surpass
the state-of-the-art on the Hipster Wars dataset despite using features only 0.3%
of the size. Our proposed features significantly outperform those obtained from
networks trained on ImageNet, despite being 32 times smaller (128 single-precision
floats), trained on noisy and weakly-labeled data, and using only 1.5% of the
number of parameters.
@InProceedings{SimoSerraCVPR2016,
author = {Edgar Simo-Serra and Hiroshi Ishikawa},
title = {{Fashion Style in 128 Floats: Joint Ranking and Classification using Weak Data for Feature Extraction}},
booktitle = "Proceedings of the Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR)",
year = 2016,
}
Structured Prediction with Output Embeddings for Semantic Image
Annotation
Ariadna Quattoni, Arnau Ramisa, Pranava Swaroop Madhyastha, Edgar Simo-Serra,
Francesc Moreno-Noguer
Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational
Linguistics: Human Language Technologies (NAACL-HLT, Short) , 2016
We address the task of annotating images with semantic tuples. Solving this problem
requires an algorithm which is able to deal with hundreds of classes for each
argument of the tuple. In such contexts, data sparsity becomes a key challenge, as
there will be a large number of classes for which only a few examples are
available. We propose handling this by incorporating feature representations of
both the inputs (images) and outputs (argument classes) into a factorized
log-linear model, and exploiting the flexibility of scoring functions based on
bilinear forms. Experiments show that integrating feature representations of the
outputs in the structured prediction model leads to better overall predictions. We
also conclude that the best output representation is specific for each type of
argument.
@InProceedings{QuattoniARXIV2016,
author = {Ariadna Quattoni and Arnau Ramisa and Pranava Swaroop Madhyastha and Edgar Simo-Serra and Francesc Moreno-Noguer},
title = {{Structured Prediction with Output Embeddings for Semantic Image Annotation}},
booktitle = "Proocedings of Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies (NAACL-HLT)"
year = 2016,
}
地球観測衛星画像上の地物自動認識
中村 良介,石井 智大,野里 博和,坂無 英徳,シモセラ エドガー,望月 義彦,飯塚 里志,石川 博
人工知能学会全国大会 , 2016
2015年
Deep learning has revolutionalized image-level tasks, e.g. image classification,
but patch-level tasks, e.g. point correspondence still rely on hand-crafted
features, such as SIFT. In this paper we use Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs)
to learn discriminant patch representations and in particular train a Siamese
network with pairs of (non-)corresponding patches. We deal with the large number of
non-corresponding patches with the combination of stochastic sampling of the
training set and an aggressive mining strategy biased towards patches that are hard
to classify. Our models are fully convolutional, efficient to compute and amenable
to modern GPUs, and can be used as a drop-in replacement for SIFT. We obtain
consistent performance gains over the state of the art, and most importantly
generalize well against scaling and rotation, perspective transformation, non-rigid
deformation, and illumination changes.
@InProceedings{SimoSerraICCV2015,
author = {Edgar Simo-Serra and Eduard Trulls and Luis Ferraz and Iasonas Kokkinos and Pascal Fua and Francesc Moreno-Noguer},
title = {{Discriminative Learning of Deep Convolutional Feature Point Descriptors}},
booktitle = "Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV)",
year = 2015,
}
In this paper, we analyze the fashion of clothing of a large social website. Our
goal is to learn and predict how fashionable a person looks on a photograph and
suggest subtle improvements the user could make to improve her/his appeal. We
propose a Conditional Random Field model that jointly reasons about several
fashionability factors such as the type of outfit and garments the user is wearing,
the type of the user, the photograph's setting (e.g., the scenery behind the user),
and the fashionability score. Importantly, our model is able to give rich feedback
back to the user, conveying which garments or even scenery she/he should change in
order to improve fashionability. We demonstrate that our joint approach
significantly outperforms a variety of intelligent baselines. We additionally
collected a novel heterogeneous dataset with 144,169 user posts containing diverse
image, textual and meta information which can be exploited for our task. We also
provide a detailed analysis of the data, showing different outfit trends and
fashionability scores across the globe and across a span of 6 years.
@InProceedings{SimoSerraCVPR2015,
author = {Edgar Simo-Serra and Sanja Fidler and Francesc Moreno-Noguer and Raquel Urtasun},
title = {{Neuroaesthetics in Fashion: Modeling the Perception of Fashionability}},
booktitle = "Proceedings of the Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR)",
year = 2015,
}
We propose a robust and efficient method to estimate the pose of a camera with
respect to complex 3D textured models of the environment that can potentially
contain more than 100,000 points. To tackle this problem we follow a top down
approach where we combine high-level deep network classifiers with low level
geometric approaches to come up with a solution that is fast, robust and accurate.
Given an input image, we initially use a pre-trained deep network to compute a
rough estimation of the camera pose. This initial estimate constrains the number of
3D model points that can be seen from the camera viewpoint. We then establish
3D-to-2D correspondences between these potentially visible points of the model and
the 2D detected image features. Accurate pose estimation is finally obtained from
the 2D-to-3D correspondences using a novel PnP algorithm that rejects outliers
without the need to use a RANSAC strategy, and which is between 10 and 100 times
faster than other methods that use it. Two real experiments dealing with very large
and complex 3D models demonstrate the effectiveness of the approach.
@InProceedings{RubioICRA2015,
author = {Antonio Rubio and Michael Villamizar and Luis Ferraz and Adri\'an Pe\~nate-S\'anchez and Arnau Ramisa and Edgar Simo-Serra and Alberto Sanfeliu and Francesc Moreno-Noguer},
title = {{Efficient Monocular Pose Estimation for Complex 3D Models}},
booktitle = "Proceedings of the International Conference in Robotics and Automation (ICRA)",
year = 2015,
}
We propose a novel kinematic prior for 3D human pose tracking that allows
predicting the position in subsequent frames given the current position. We first
define a Riemannian manifold that models the pose and extend it with its Lie
algebra to also be able to represent the kinematics. We then learn a joint Gaussian
mixture model of both the human pose and the kinematics on this manifold. Finally
by conditioning the kinematics on the pose we are able to obtain a distribution of
poses for subsequent frames that which can be used as a reliable prior in 3D human
pose tracking. Our model scales well to large amounts of data and can be sampled at
over 100,000 samples/second. We show it outperforms the widely used Gaussian
diffusion model on the challenging Human3.6M dataset.
@InProceedings{SimoSerraMVA2015,
author = {Edgar Simo-Serra and Carme Torras and Francesc Moreno-Noguer},
title = {{Lie Algebra-Based Kinematic Prior for 3D Human Pose Tracking}},
booktitle = "International Conference on Machine Vision Applications (MVA)",
year = 2015,
}
Recent advances in 3D shape analysis and recognition have shown that heat diffusion
theory can be effectively used to describe local features of deforming and scaling
surfaces. In this paper, we show how this description can be used to characterize
2D image patches, and introduce DaLI, a novel feature point descriptor with high
resilience to non-rigid image transformations and illumination changes. In order to
build the descriptor, 2D image patches are initially treated as 3D surfaces.
Patches are then described in terms of a heat kernel signature, which captures both
local and global information, and shows a high degree of invariance to non-linear
image warps. In addition, by further applying a logarithmic sampling and a Fourier
transform, invariance to photometric changes is achieved. Finally, the descriptor
is compacted by mapping it onto a low dimensional subspace computed using Principal
Component Analysis, allowing for an efficient matching. A thorough experimental
validation demonstrates that DaLI is significantly more discriminative and robust
to illuminations changes and image transformations than state of the art
descriptors, even those specifically designed to describe non-rigid deformations.
@Article{SimoSerraIJCV2015,
author = {Edgar Simo-Serra and Carme Torras and Francesc Moreno Noguer},
title = {{DaLI: Deformation and Light Invariant Descriptor}},
journal = {International Journal of Computer Vision (IJCV)},
volume = {115},
number = {2},
pages = {136--154},
year = 2015,
}
2014年
In this paper we tackle the problem of semantic segmentation of clothing. We frame
the problem as the one of inference in a pose-aware Markov random field which
exploits appearance, figure/ground segmentation, shape and location priors for each
garment as well as similarities between segments and symmetries between different
human body parts. We demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach in the
fashionista dataset and show that we can obtain a significant improvement over the
state-of-the-art.
@InProceedings{SimoSerraACCV2014,
author = {Edgar Simo-Serra and Sanja Fidler and Francesc Moreno-Noguer and Raquel Urtasun},
title = {{A High Performance CRF Model for Clothes Parsing}},
booktitle = "Proceedings of the Asian Conference on Computer Vision (ACCV)",
year = 2014,
}
We present a novel approach for learning a finite mixture model on a Riemannian
manifold in which Euclidean metrics are not applicable and one needs to resort to
geodesic distances consistent with the manifold geometry. For this purpose, we draw
inspiration on a variant of the expectation-maximization algorithm, that uses a
minimum message length criterion to automatically estimate the optimal number of
components from multivariate data lying on an Euclidean space. In order to use this
approach on Riemannian manifolds, we propose a formulation in which each component
is defined on a different tangent space, thus avoiding the problems associated with
the loss of accuracy produced when linearizing the manifold with a single tangent
space. Our approach can be applied to any type of manifold for which it is possible
to estimate its tangent space. In particular, we show results on synthetic examples
of a sphere and a quadric surface and on a large and complex dataset of human
poses, where the proposed model is used as a regression tool for hypothesizing the
geometry of occluded parts of the body.
@InProceedings{SimoSerraBMVC2014,
author = {Edgar Simo-Serra and Carme Torras and Francesc Moreno-Noguer},
title = {{Geodesic Finite Mixture Models}},
booktitle = "Proceedings of the British Machine Vision Conference (BMVC)",
year = 2014,
}
This paper presents a methodology for the description and finite-position
dimensional synthesis of articulated systems with multiple end-effectors. The
articulated system is represented as a rooted tree graph. Graph and dimensional
synthesis theories are applied to determine when exact finite-position synthesis
can be performed on the tree structures by considering the motion for all the
possible subgraphs. Several examples of tree topologies are presented and
synthesized. This theory has an immediate application on the design of novel
multi-fingered hands.
@Article{SimoSerraMAMT2014,
author = {Edgar Simo-Serra and Alba Perez-Gracia},
title = {{Kinematic Synthesis using Tree Topologies}},
journal = {Mechanism and Machine Theory},
volume = {72},
pages = {94--113},
year = 2014,
}
2013年
We introduce a novel approach to automatically recover 3D human pose from a single
image. Most previous work follows a pipelined approach: initially, a set of 2D
features such as edges, joints or silhouettes are detected in the image, and then
these observations are used to infer the 3D pose. Solving these two problems
separately may lead to erroneous 3D poses when the feature detector has performed
poorly. In this paper, we address this issue by jointly solving both the 2D
detection and the 3D inference problems. For this purpose, we propose a Bayesian
framework that integrates a generative model based on latent variables and
discriminative 2D part detectors based on HOGs, and perform inference using
evolutionary algorithms. Real experimentation demonstrates competitive results, and
the ability of our methodology to provide accurate 2D and 3D pose estimations even
when the 2D detectors are inaccurate.
@InProceedings{SimoSerraCVPR2013,
author = {Edgar Simo-Serra and Ariadna Quattoni and Carme Torras and Francesc Moreno-Noguer},
title = {{A Joint Model for 2D and 3D Pose Estimation from a Single Image}},
booktitle = "Proceedings of the Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR)",
year = 2013,
}
2012年
In this paper we present a novel method of designing multi-fingered robotic hands
using tasks composed of both finite and infinitesimal motion. The method is based
on representing the robotic hands as a kinematic chain with a tree topology. We
represent finite motion using Clifford algebra and infinitesimal motion using Lie
algebra to perform finite dimensional kinematic synthesis of the multi-fingered
mechanism. This allows tasks to be defined not only by displacements, but also by
the velocity and acceleration at different positions for the design of robotic
hands. An example task is provided using an experimental motion capture system and
we present the design of a robotic hand for the task using a hybrid Genetic
Algorithm/Levenberg-Marquadt solver.
@InProceedings{SimoSerraARK2012,
author = {Edgar Simo-Serra and Alba Perez-Gracia and Hyosang Moon and Nina Robson},
title = {{Kinematic Synthesis of Multi-Fingered Robotic Hands for Finite and Infinitesimal Tasks}},
booktitle = "Advances in Robot Kinematics (ARK)",
year = 2012,
}
Markerless 3D human pose detection from a single image is a severely
underconstrained problem in which different 3D poses can have very similar image
projections. In order to handle this ambiguity, current approaches rely on prior
shape models whose parameters are estimated by minimizing image-based objective
functions that require 2D features to be accurately detected in the input images.
Unfortunately, although current 2D part detectors algorithms have shown promising
results, their accuracy is not yet sufficiently high to subsequently infer the 3D
human pose in a robust and unambiguous manner. We introduce a novel approach for
estimating 3D human pose even when observations are noisy. We propose a stochastic
sampling strategy to propagate the noise from the image plane to the shape space.
This provides a set of ambiguous 3D shapes, which are virtually undistinguishable
using image-based information alone. Disambiguation is then achieved by imposing
kinematic constraints that guarantee the resulting pose resembles a 3D human shape.
We validate our approach on a variety of situations in which state-of-the-art 2D
detectors yield either inaccurate estimations or partly miss some of the body
parts.
@InProceedings{SimoSerraCVPR2012,
author = {Edgar Simo-Serra and Arnau Ramisa and Guillem Aleny\`a and Carme Torras and Francesc Moreno-Noguer},
title = {{Single Image 3D Human Pose Estimation from Noisy Observations}},
booktitle = "Proceedings of the Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR)",
year = 2012,
}
2011年
In this paper, we explore the idea of designing non-anthropomorphic, multi-fingered
robotic hands for tasks that replicate the motion of the human hand. Taking as
input data rigid-body trajectories for the five fingertips, we develop a method to
perform dimensional synthesis for a kinematic chain with a tree structure, with
three common joints and five branches. We state the forward kinematics equations of
relative displacements for each serial chain expressed as dual quaternions, and
solve for up to five chains simultaneously to reach a number of poses along the
hand trajectory using a hybrid global numerical solver that integrates a genetic
algorithm and a Levenberg-Marquardt local optimizer. Although the number of
candidate solutions in this problem is very high, the use of the genetic algorithm
lets us to perform an exhaustive exploration of the solution space and retain a
subset of them. We then can choose some of the solutions based on the specific task
to perform. Note that these designs could match the task exactly while having a
finger design radically different from that of the human hand.
@InProceedings{SimoSerraIDETC2011,
author = {Edgar Simo-Serra and Francesc Moreno-Noguer and Alba Perez-Gracia},
title = {{Design of Non-Anthropomorphic Robotic Hands for Anthropomorphic Tasks}},
booktitle = "Proceedings of the 2011 ASME International Design Engineering Technical Conferences",
year = 2011,
}